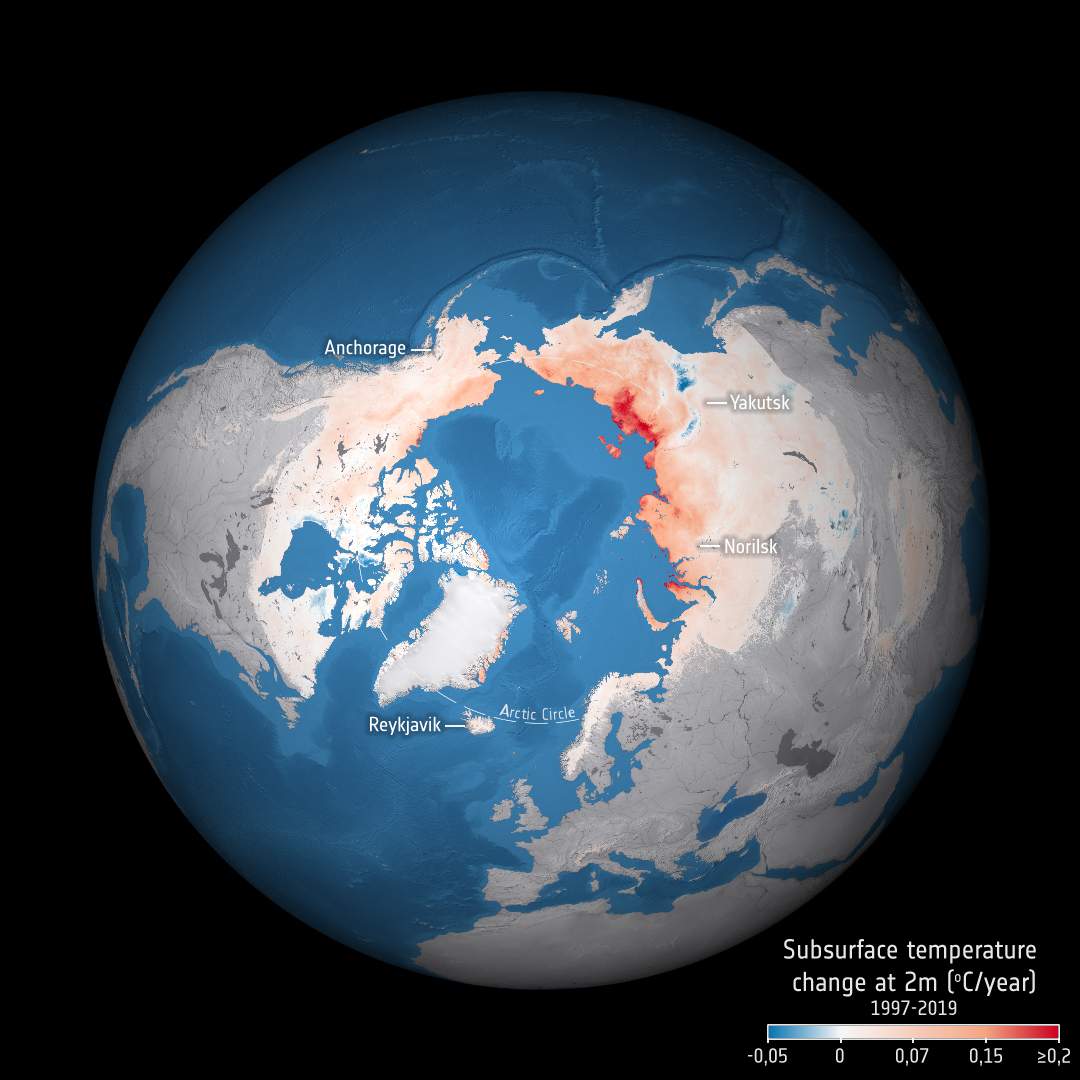

The Arctic is warming more than twice as fast as the global average, making climate change’s polar effects more intense than anywhere else in the world. The Arctic accounts for half of the organic carbon stored in soils. There is high confidence that the thaw of terrestrial permafrost will lead to carbon release, but only low confidence regarding timing, magnitude and relative role of CO2 versus CH4 according to the sixth assessment report of IPCC (2021). There is general consensus that these issues can be tackled through support by satellite observations, but this has not been fully exploited to date. The recently inaugurated Arctic Methane and Permafrost Challenge (AMPAC) strives to address these questions inter alia through making use of synergistic measurements, activities to improve satellite retrievals with a clear focus on high latitudes, and promoting new dedicated satellite sensors as well as improving validation of existing and upcoming satellite missions.
AMPAC-Net partners represent experts in remote sensing (terrestrial and atmosphere), in situ measurements in permafrost environments and geospatial data dissemination in order to facilitate activities encompassing gap analyses, data collection, benchmarking and Bottom-up Top-down synthesis.
b.geos GmbH
Österreich
© b.geos GmbH | 2024